Chemistry
Chemistry is the study of matter, its properties, how and why substances combine or separate to form other substances, and how substances interact with energy. Many people think of chemists as being white-coated scientists mixing strange liquids in a laboratory, but the truth is we are all chemists.
Doctors, nurses and veterinarians must study chemistry, but understanding basic chemistry concepts is important for almost every profession. Chemistry is part of everything in our lives.
Every material in existence is made up of matter — even our own bodies. Chemistry is involved in everything we do, from growing and cooking food to cleaning our homes and bodies to launching a space shuttle. Chemistry is one of the physical sciences that help us to describe and explain our world.
GCSE Chemistry
Chemistry gives students the opportunity to gain a fuller understanding of:
- the nature of substances and how they react together
- how Chemistry is used in business and industry
- how our use of raw materials in fuels and manufacturing can affect the global and local environment.
The Chemistry GCSE is designed to help students understand how to formulate a scientific approach to understanding and explaining the world and solving problems. This means that the 'How Science Works' approach is integrated throughout the GCSE.
The course has been structured in a way that starts with the fundamental ideas in Chemistry, putting the building blocks in place. This enables students to develop an understanding of topics such as chemical structures and their properties, chemical reactions and how to analyse substances.
During their time studying Chemistry at NUAST pupils will look at substances that they will come across in their daily lives like drinking water, vegetable oils and metals, our aim is to engage students by putting their learning in context.
Exam Board: AQA
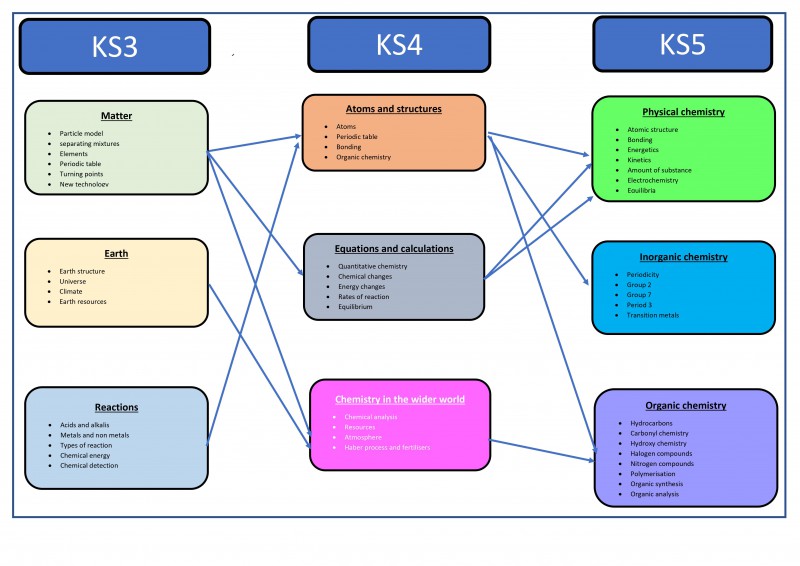
Course break down
- Atomic structure and the periodic table
- Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
- Quantitative chemistry
- Chemical changes
- Energy changes
- The rate and extent of chemical change
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical analysis
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
Revision materials
A-Level Chemistry
A-level Chemistry is a rigorous, challenging and ultimately rewarding course that develops students' scientific skills and knowledge.
There are three disciplines of chemistry studied within the A-level course: Physical chemistry, inorganic chemist and organic chemistry.
Inorganic chemistry looks at the periodic table and how it is structured. It looks at the organisation of the known chemical elements and how chemist can make sense of their physical and chemical properties. The topics studied in inorganic chemistry are:
- Periodicity
- Group 2, the Alkaline Earth Metals
- Group 7, the Halogens
- Period 3 elements and their oxides
- The transition metals
- Reactions of inorganic compounds in aqueous solutions
Physical Chemistry looks at the chemical properties of elements depending on their atomic structure and in particular on the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. The topics studied in physical chemistry are:
- Atomic structure
- Amount of substance
- Bonding
- Energetics
- Kinetics
- Equilibria
- Oxidation, reduction and redox reactions
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetics
- Equilibrium Constant Kp
- Electrode potentials and electrochemical cells
- Acids, bases and buffers
Organic Chemistry delves into the study of the millions of covalent compounds of the element carbon. These structurally diverse compounds vary from naturally occurring petroleum fuels to DNA and the molecules in living systems. Organic chemistry also looks at the development of drugs, medicines and plastics. The topics studied in organic chemistry are:
- Introduction to organic chemistry
- Alkanes
- Halogenoalkanes
- Alkenes
- Alcohols
- Organic Analysis
- Nomenclature and isomerism
- Compounds containing the carbonyl group
- Aromatic chemistry
- Amines
- Polymerisation
- Amino acids, proteins and DNA
- Organic synthesis and analysis
- Structure determination
- Chromatography
Assessment in A level chemistry is spread over three papers at the end of year 13. Throughout year 12 and 13 students will also complete a minimum of 12 practicals to show competency at a range of practical skills, techniques and apparatus. Some practical activities include:
- Measurement of an enthalpy change
- Tests for alcohol, aldehyde, alkene and carboxylic acid.
- Measuring the rate of reaction.
- Preperation of an organic solid (aspirin) and organic liquid
- Thin layer chromatography
- Carry out simple test-tube reactions to identify transition metal ions in aqueous solution.
- And many more…
Science News
- Y10 Girls in Physics trip
Some lucky NUAST students attended a day hosted by The University of Nottingham. (13/07/2018) - Rocket trip at Kimberly school
The trip was organised by the University of Nottingham and the Ogdon trust. (21/06/2018) - Y12 Chemists educational visit to The University of Nottingham
Chemistry lectures and thunder and lightning demonstrations (24/01/2017) - NUAST students come second from 200 schools!
Chemistry Challenge (20/01/2016)


